How to use tiny indel markers
The following are the results of research conducted in collaboration with Dr. Takahiro Noda (Kumamoto Prefectural Agricultural Research Center) and his colleagues . We published the results as an open access paper as follows.
Noda, T., Daiou, K., Mihara, T., & Nagano, Y. (2020). Development of Indel markers for the selection of Satsuma mandarin (Citrus unshiu Marc.) hybrids that can be used for low-cost genotyping with agarose gels. Euphytica, 216:115.
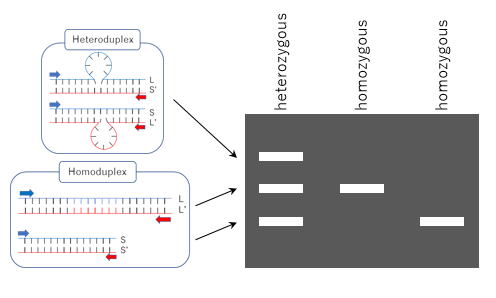
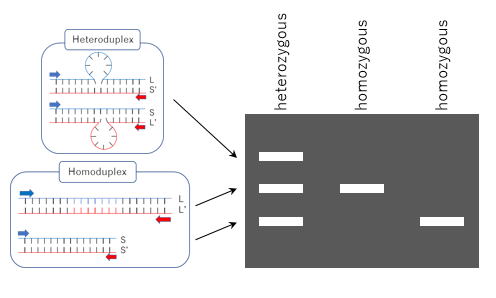
We have developed this research method to select the Satsuma mandarin x Satsuma mandarin. However, we show this method here because it has the potential to be used in animals, plants and microorganisms.
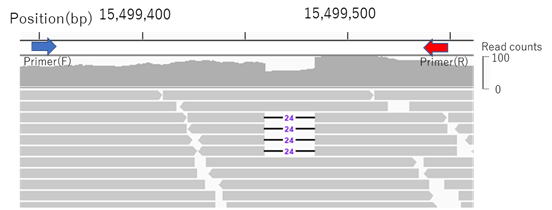
Requirements: Organisms with a high number of tiny indel markers (20-30 bp) are eligible for this method.

For 1 and 2 above, we may support researchers in developing countries. (Contact information: Dr. Yukio Nagano, Saga University, nagano@cc.saga-u.ac.jp)
Primer sequences for Citrus species ara available here.
Tiny indel markersの活用法
熊本県農業研究センターの野田孝博博士らと共同で行った研究の成果を紹介します。この成果は、以下にオープンアクセスの論文として、発表しています。
Noda, T., Daiou, K., Mihara, T., & Nagano, Y. (2020). Development of Indel markers for the selection of Satsuma mandarin (Citrus unshiu Marc.) hybrids that can be used for low-cost genotyping with agarose gels. Euphytica, 216:115.
ウンシュウミカン×ウンシュウミカンを選抜するために、この研究方法を開発しました。しかし、動物・植物・微生物に幅広く活用できる可能性があるため、ここに紹介します。
必要条件:20-30 bpくらいのtiny indel markersの多い生物がこの方法の適用対象となります。

3は出来そうだけど、1と2が難しいと感じる方が多いかもしれません。1と2については、共同研究が実施可能な場合がありますので、佐賀大学・永野幸生 nagano@cc.saga-u.ac.jp までご連絡ください。
カンキツ用のプライマー配列はこちらで確認できます。